|
|
 |
General Scientific Information
- When pure, thorium is a silvery white metal which is air-stable and retains its lustre
for several months.
- When contaminated with the oxide, thorium slowly tarnishes in air, becoming grey and
finally black.
- Thorium oxide has a melting point of 3300°C, the highest of all oxides. Only a few
elements, such as tungsten, and a few compounds, such as tantalum carbide, have higher
melting points.
- Thorium is slowly attacked by water, but does not dissolve readily in most common acids,
except hydrochloric.
- Powdered thorium metal is often pyrophoric and should be carefully handled.When heated
in air, thorium turnings ignite and burn brilliantly with a white light.
- Monazite - phosphate mineral [(Ce,La,Y,Th)PO4], found in the form of sand in
the U.S., Madagascar, Brazile, India, Sri Lanka and Australia. Monazite is an important source
of Cerium, Thorium and other Rare-Earth
Metals.
| Atomic Structure |
| Atomic Number |
90 |
| Atomic Weight |
232.0381 |
| No. of Electrons Shells |
7 |
| Periodic Chart Group |
Actinide (Group IIIb) |
| Classification |
Rare Earth |
| Physical Properties |
| Symbol: |
Th |
| Melting Point: |
1750.0 oC |
| Boiling Point: |
4790.0 oC |
| Density @ 293 K: |
11.72 g/cm3 |
| Electrical resistivity |
15E-8 Siemens |
| Velocity of Sound |
2490 m/s |
| Appearance |
soft, ductile, lustrous, silvery-white |
| CAS Registry Number: |
7440-29-1 |
| Chemical Properties |
| Electron Valence State |
+4 |
| Molar Volume |
19.80 cm3 |
| Crystal Structure @ 20 C |
face-centered cubic |
| Additional Information |
Thorium |
THORIUM ATOMIC ELECTRON CONFIGURATION
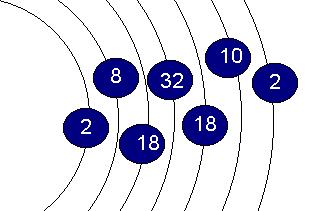
The following represents the electronic configuration and its associated
term symbol for the ground state neutral gaseous atom. The configuration associated
with thorium in its compounds is not necessarily the same.
| thorite |
A rare mineral, thorium silicate, ThSiO4,
occurring in the form of a yellow or black crystal |
| thorianite |
A rare mineral, mainly thoria, ThO2, but also
containing uranium, cerium and other rare-earth metals. Thorianite is found as
small, black cubic crystals and is a source of thorium. |
| THERMODYNAMIC DATA |
| State |
DfH°
/kJ mol-1 |
DfG°
/kJ mol-1 |
S°
/J K-1 mol-1 |
CpH
/J K-1 mol-1 |
H°298.15-H°0
/kJ mol-1 |
| Solid |
*0 |
0 |
*51.8 ± 0.5 |
27.3 |
|
| Gas |
*602 ± 6 |
561 |
*190.17 ± 0.05 |
20.8 |
|
Notes
These tables give a few thermodynamic
data. Most values are those given in the NBS technical notes (reference 1) after
conversion from the units used within those notes. Values labelled with an asterisk (*)
are Committee on Data for Science and Technology (CODATA) agreed values for
the thermodynamic properties of key chemical substances (reference 2). These values are
published in a number of places including the WWW (reference 3)
R.H. Schumm, D.D. Wagman, S. Bailey, W.H. Evans, and V.B. Parker in
National Bureau of Standards (USA) Technical Notes 270-1 to 270-8, 1973.
J.D. Cox, DD., Wagman, and V.A. Medvedev, CODATA Key Values for
Thermodynamics, Hemisphere Publishing Corp., New York, USA, 1989.
http://www.codata.org/programs/codata/databases/key1.html
|
|



